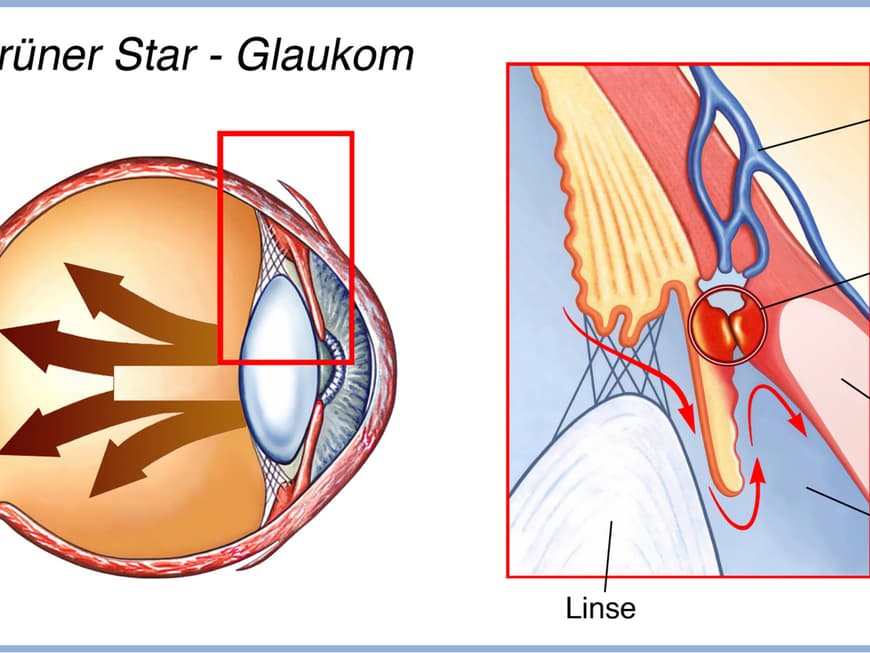
What is glaucoma?
In glaucoma, more aqueous humor is produced in the eye than can drain away - this causes the intraocular pressure to rise and sensitive visual and sensory cells in the retina and optic nerve to die. As a result, the field of vision narrows until only a small section can be seen, leading to the risk of blindness.
On average, around four percent of all people develop glaucoma during their lifetime. Women are affected more often than men.
How can glaucoma be detected?
This is why ophthalmologists advise having the intraocular pressure, the back of the eye and the optic nerve checked regularly. This IGeL service costs 20 to 40 euros. The risk of developing the disease increases with age. From the age of 40, you should have an examination every two to five years.
Eye drops can reduce intraocular pressure. There are now new procedures that help patients. One of these is "iStent inject" - one of the world's smallest implants.
The system consists of two stents that are inserted into the anterior chamber of the eye in a microinvasive procedure. The aqueous humor is guided through the stents directly into its natural drainage pathway, reducing intraocular pressure. The procedure is covered by the health insurance.